GTM (Google Tag Manager)
When running a website, it is essential to utilize various tools. Applying these tools often requires adding meta data or JavaScript to the site. While it is possible to manage this using a CMS, using a versatile tool like Google Tag Manager allows for more flexible and efficient operations.
This document outlines the steps to apply Google Tag Manager to a Next.js project.
Next.js Pages Router
Here, we introduce a sample using the Next.js Page Router. For the latest information, please refer to the Next.js official site.
Let’s create a sample project.
-
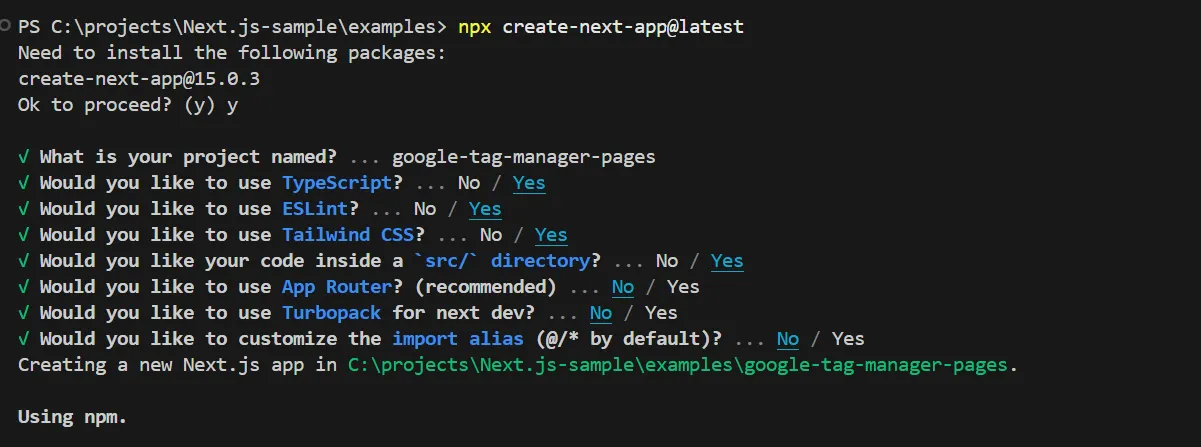
Create a Next.js project.
Terminal window npx create-next-app@latestAnswer the prompts to create a Pages Router project as shown below.
-
Next, install the package
@next/third-parties@latest.Terminal window npm install @next/third-parties@latest -
Add code to
/pages/_app.tsxto make it available globally./pages/_app.tsx import '@/styles/globals.css';import type { AppProps } from 'next/app';import { GoogleTagManager } from '@next/third-parties/google';export default function App({ Component, pageProps }: AppProps) {return (<><Component {...pageProps} /><GoogleTagManager gtmId="GTM-XYZ" /></>);} -
When you start the project, you can confirm that the Google Tag Manager code has been added.
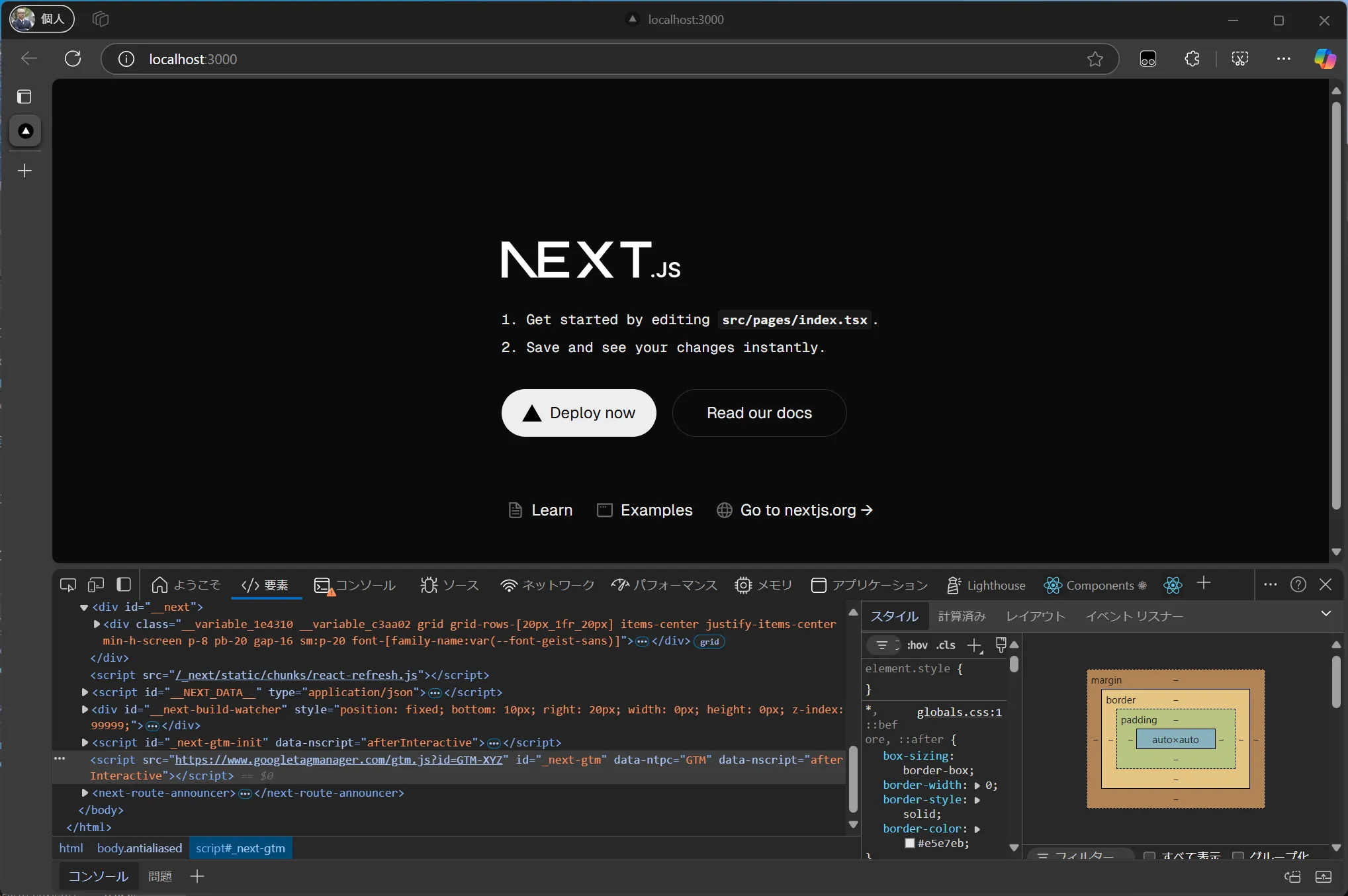
-
To manage the GTM key using environment variables, create a
.env.localfile and write the following:/.env.local NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_TAG_MANAGER=<your API key here> -
To load the key written in
.env.local, modify the following file:/pages/_app.tsx export default function App({ Component, pageProps }: AppProps) {return <><Component {...pageProps} /><GoogleTagManager gtmId={process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_TAG_MANAGER || ""} /></>
The sample code introduced above can be referenced from the following repository.
Next.js App Router
Here, we introduce a sample using the Next.js App Router. For the latest information, please refer to the Next.js official site.
-
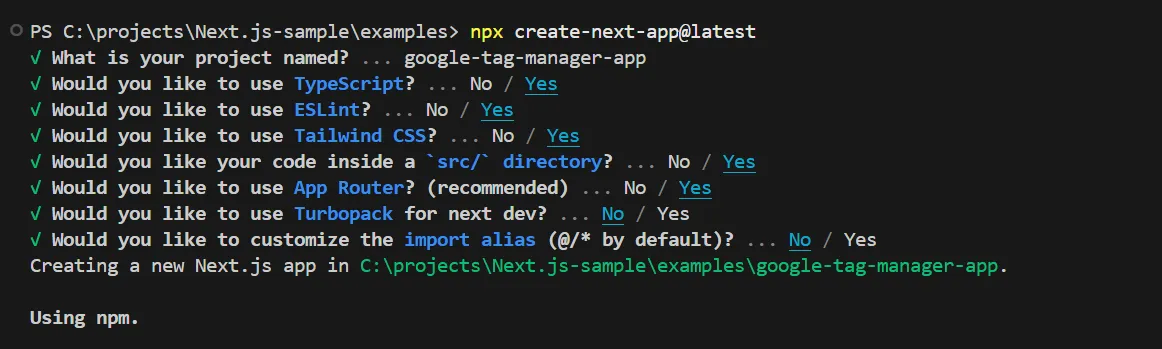
Create a Next.js project.
Terminal window npx create-next-app@latestAnswer the prompts to create a Pages Router project as shown below.
-
Next, install the package
@next/third-parties@latest.Terminal window npm install @next/third-parties@latest -
Add code to
/app/layout.tsxto make it available globally./app/layout.tsx import { GoogleTagManager } from '@next/third-parties/google';import type { Metadata } from 'next';import localFont from 'next/font/local';import './globals.css';const geistSans = localFont({src: './fonts/GeistVF.woff',variable: '--font-geist-sans',weight: '100 900',});const geistMono = localFont({src: './fonts/GeistMonoVF.woff',variable: '--font-geist-mono',weight: '100 900',});export const metadata: Metadata = {title: 'Create Next App',description: 'Generated by create next app',};export default function RootLayout({children,}: Readonly<{children: React.ReactNode;}>) {return (<html lang="en"><GoogleTagManager gtmId="GTM-XYZ" /><body className={`${geistSans.variable} ${geistMono.variable} antialiased`}>{children}</body></html>);} -
When you start the project, you can confirm that the Google Tag Manager code has been added.
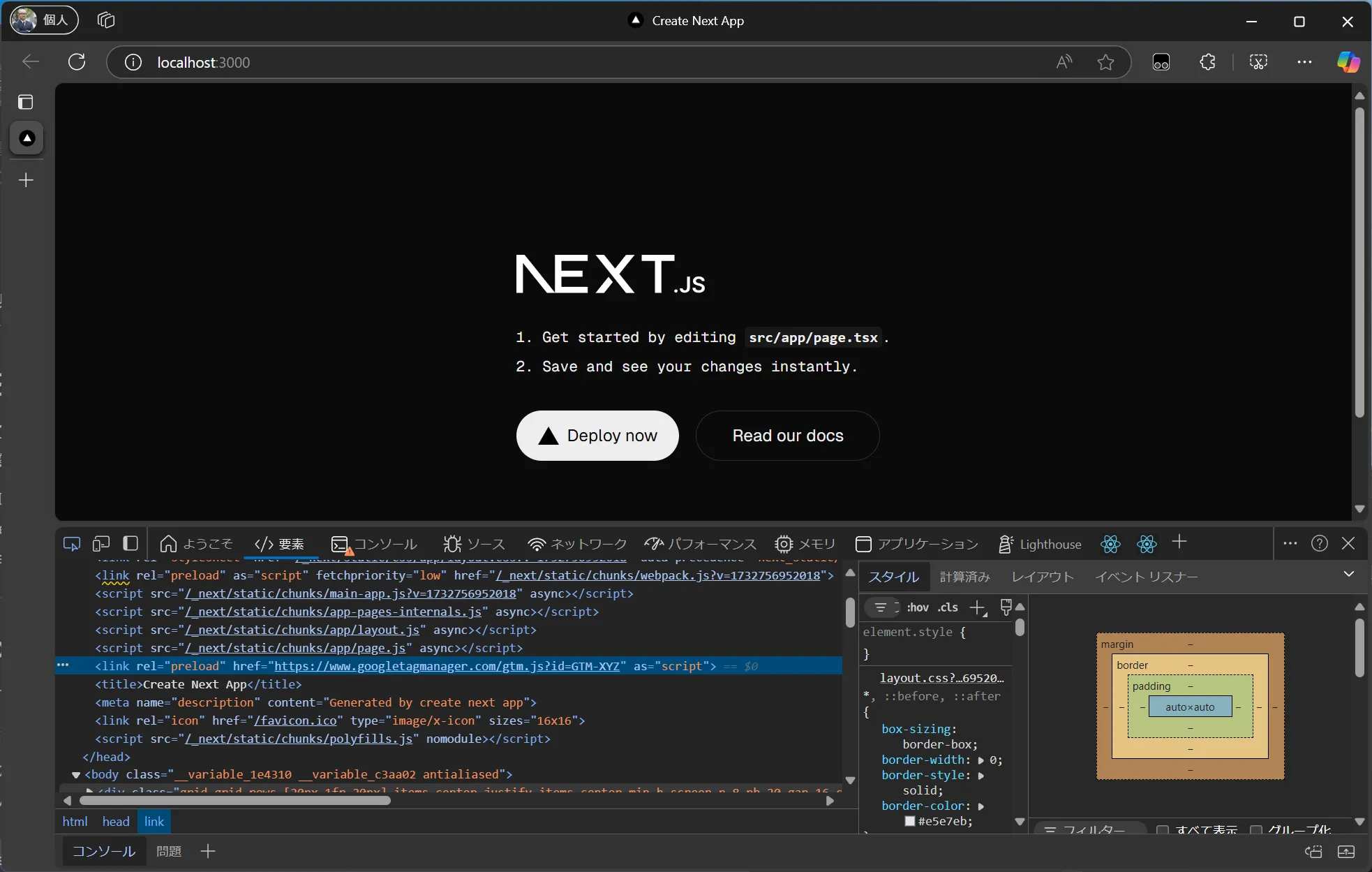
-
To manage the GTM key using environment variables, create a
.env.localfile and write the following:/.env.local NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_TAG_MANAGER=<your API key here> -
To load the key written in
.env.local, modify the following file:/app/layout.tsx return (<html lang="en"><GoogleTagManager gtmId={process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_TAG_MANAGER || ""} /><bodyclassName={`${geistSans.variable} ${geistMono.variable} antialiased`}>{children}
The sample code introduced above can be referenced from the following repository.
Other Implementations
Previously, I introduced the implementation of GTM in Next.js using a package called react-gtm-module.
There are other packages available for integrating GTM, but the steps provided by Next.js are the simplest, so I will omit the details of other implementations.
Summary
The implementation of Google Tag Manager is already provided in the official Next.js documentation. Please refer to the official steps in addition to this document.